Published: Oct 8, 2014 by The PISM Authors
In a new Nature Communications paper, researchers at Victoria University and the University of New South Wales describe a model study of Antarctic ice sheet evolution over the last 25 kyr using PISM with ocean-forcing inputs from the Earth system model LOVECLIM. They show that when the ocean around Antarctica becomes more stratified, warm water at depth melts the ice sheet faster than when the ocean is less stratified.
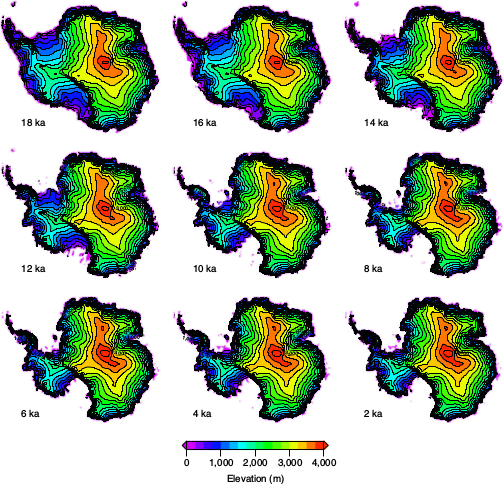
The study used a large ensemble of 15 km PISM simulations in a data-constrained mode. In the simulations that best fit a variety of temporal and spatial observations, several episodes of accelerated ice-sheet recession occurred, with the timing of the largest being coincident with meltwater pulse 1A. This episode saw an abrupt rise in global sea level, with an Antarctic contribution of nearly three meters over just a few centuries.
Both this blog entry and this Science Daily news item summarize the work and relate the modeled melt from 14,000 years ago to present-day Antarctic conditions.
